The validation offers the possibility to check a data set according to given guidelines. These guidelines are defined in a producttype, which must be available as valid JSON. Depending on whether the guidelines/conditions in the producttype are fulfilled, a record appears on the output “successful” or “failed”. For example, attributes can be checked for “being present” or in the correct format.
First an example for the attribute “product_id”:
[{
“key”: “product_id”,
“name”: null,
“description”: null,
“attributeType”: “text”,
“pattern”: null,
“fixedValues”: null,
“defaultValue”: null,
“attributeSortingHint”: 20,
“unit”: null,
“isMandatory”: true,
“isVariantAttribute”: false,
“attributeGroup”: null,
“attributeGroupSortingHint”: null.
}]
| key | possible values | comment |
|---|---|---|
| key | attributename | which attribute to check |
| name | any value/text | (localized) attribute name |
| description | any value/text | (localized) description |
| attributeType | text / number / date | What type must the attribute be |
| pattern | regularExpression | which pattern must be matched |
| fixedValues | a list of values that are allowed | e.g. [‘1’,‘2’,‘7’], all other values lead to “faulty” |
| defaultValue | An arbitrary value/text | If the attribute is empty this value will be entered |
| attributeSortingHint | Any integer | The attributes in the producttype are sorted by these numbers |
| unit | Any value/text | A unit can be forced |
| isMandatory | true / false | If the attribute is mandatory |
| attributeGroup | Any value | The attribute is assigned to a group |
| attributeGroupSortingHint | Any integer | The groups are sorted by these numbers |
| If the value ‘null’ is specified, the line is ignored and skipped during the check. |
Example for the key ‘pattern’: "([0-9a-zA-Z\\._-]+\\.(png|PNG|gif|GIF|jp[e]?g|JP[E]?G))".
The opening and closing slashes are not required. A backslash must be escaped twice \\.
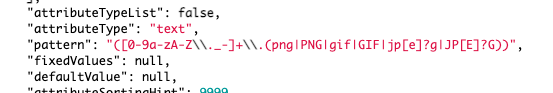
Such a scheme can be stored under the “Scheme” tab:
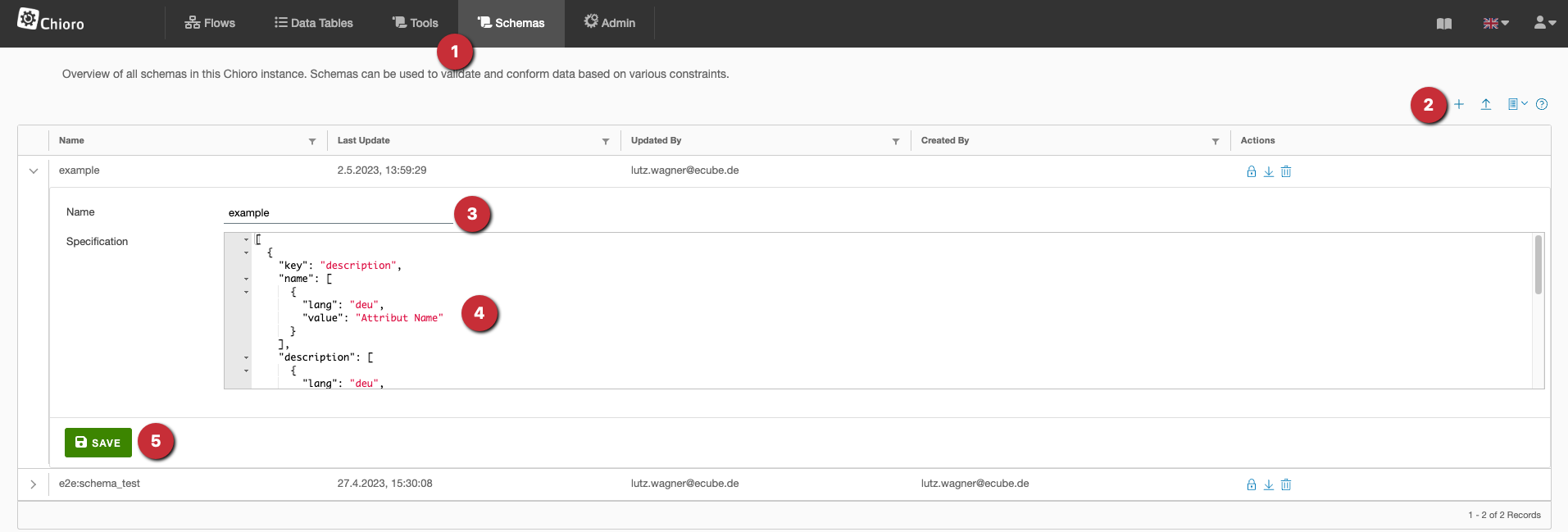
- the tab “Produkttyp”
- with the “Plus” button a new producttype is added
- a name must be given to the producttype
- here is the producttype itself, an example JSON is given.
- After clicking on “Save” the producttype can be used in the validation.
Now it continues in the desired flow:
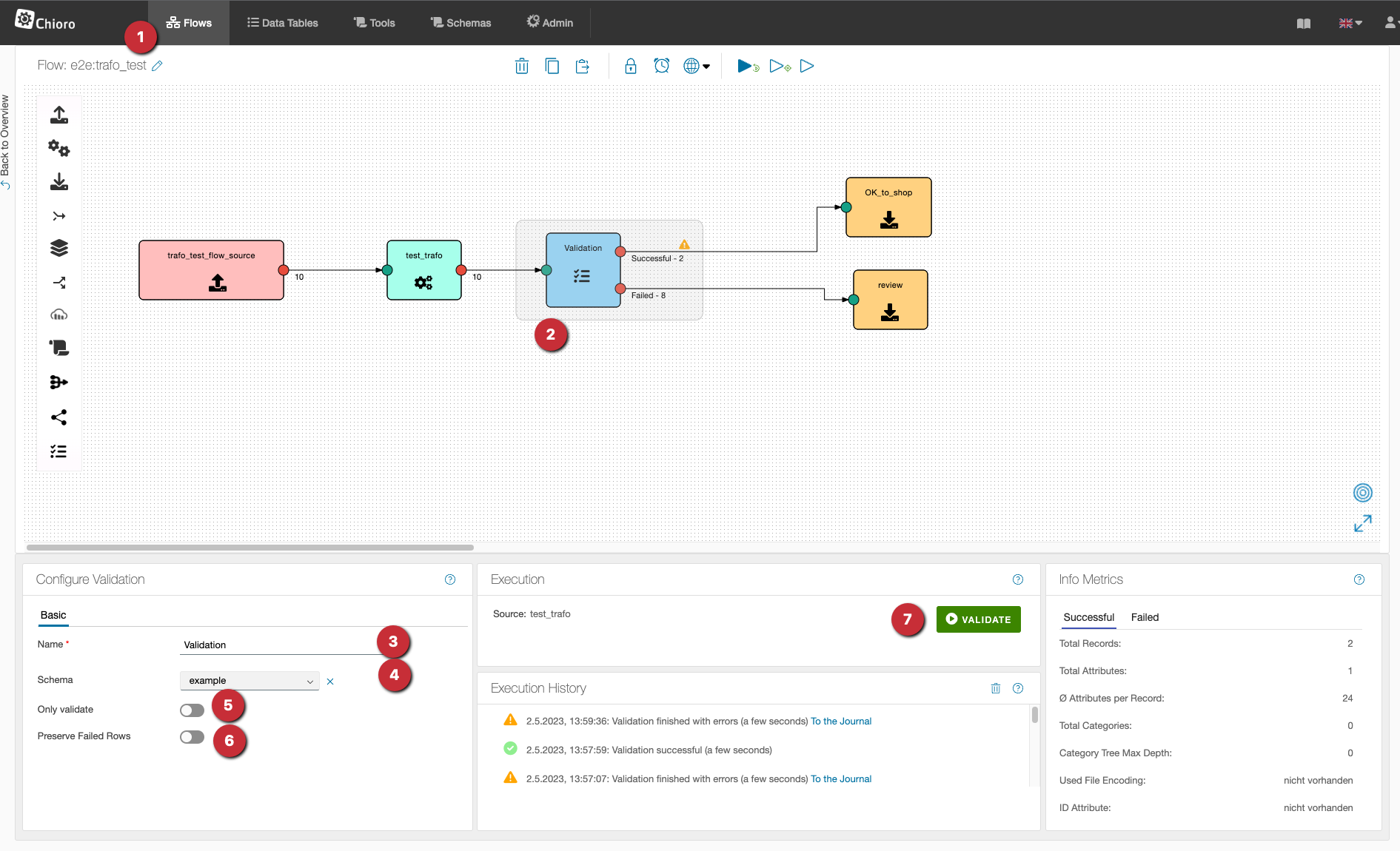
- the tab “Flows
- from the toolbar on the left you can insert a new Validation
- the validation needs a name
- from the drop-down menu the desired scheme is selected
- “Only validate” button
“Off”: Attributes/columns that do not fulfill the producttype will be removed from the dataset.
“On”: Attributes/columns that do not fulfill the producttype are kept and only marked as incorrect. - “Preserve Failed Rows” button
“Off”: rows/data records that do not meet the conditions of the producttype will be deleted
“On”: rows/data records that do not meet the conditions of the producttype are only marked as faulty. - if the settings have been made, the validation is started here.
Custom Validation Tools
Sometimes the validation features of the producttype is not enough to cover some complex usecases. In these scenarios, the user can define a custom tool to achieve this. The tool under the Validation Section has the same syntax as the Toolbox and works based on the same mechanism, however the chioro producttypes require certain type of objects to be returned from the tools to work properly. The format of these object is described below using an example:
Assuming that we have a name attribute which can contain a nested object with the firstName and lastName properties and assuming that both first name and last name should exist, we can define the following validation tool to validate these sort of attributes.
Sample data:
| id | name | expected errors |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | {firstName: ‘lutz’, lastName: ‘wagner’} | none |
| 2 | ‘lutz wagner’ | first name is not defined, last name is not defined |
| 3 | {‘lastName’: ‘wagner’} | first name is not defined |
Sample Tool (name = nameValidator):
function (key) {
let attributeValue = source(key);
if(!attributeValue.firstName) {
return {"errors":["first name is not defined"]}
}
if(!attributeValue.lastName) {
return {"errors":["last name is not defined"]}
}
}
For the sample tool above, the producttype has to be configured as follows:
[{
“key”: “name”,
… other attributes same as the example above
“customValidation”: “nameValidator” <===
}]