Other ‣ Examples ‣ Multi Rule
The multi-rule can process any number of attributes and, like the variable rule, write them to a dynamically generated target attribute. The source attribute is selected using direct specifications, placeholders or regular expressions. The target attribute in turn uses a tool or a JavaScript instruction to generate it.
For example, an underscore and the date are appended to the color and decription columns:
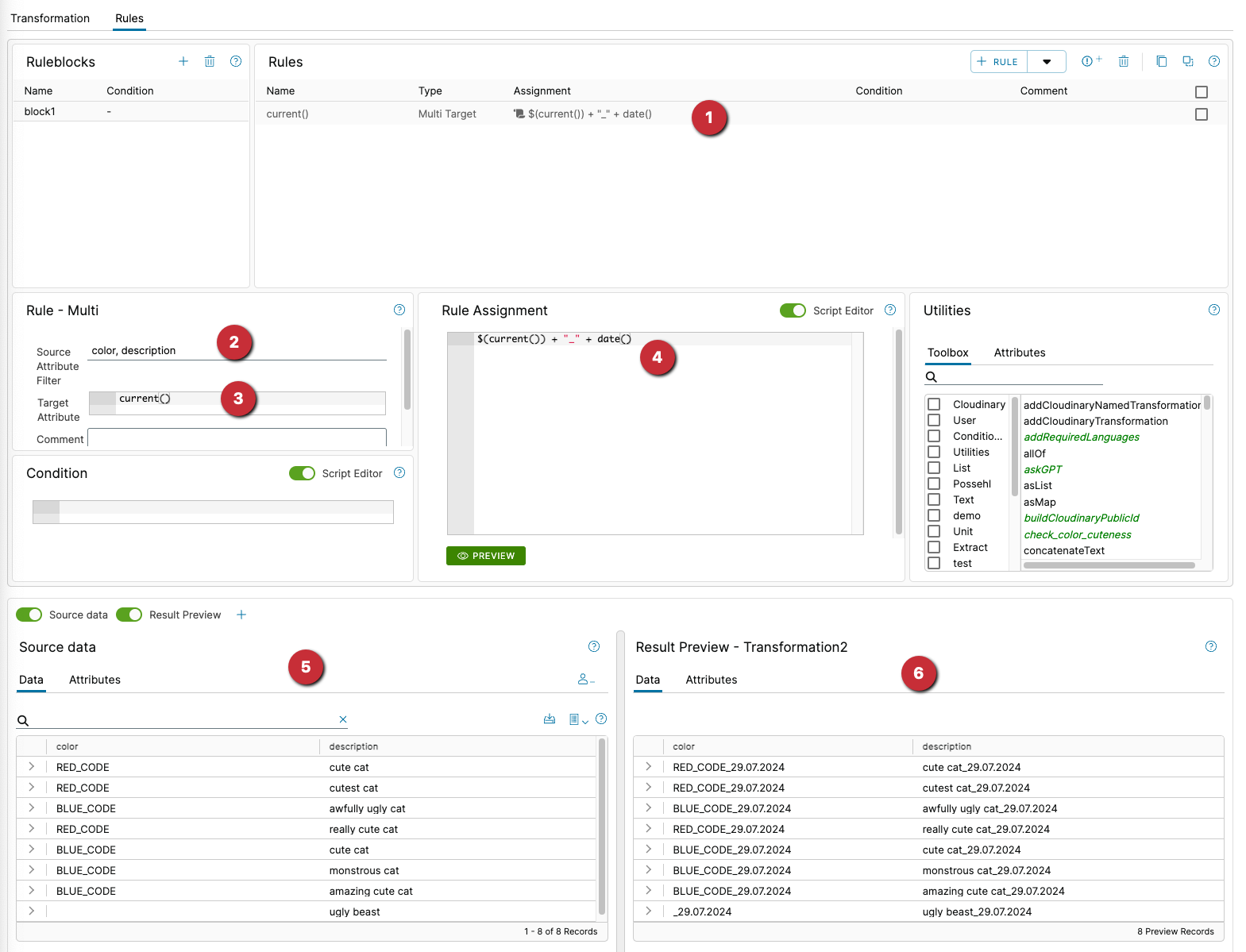
- the rule in the rule list
- two source attributes are fetched one after the other,
coloranddescription. Thencoloris processed first, followed bydescription. current()in the target attribute means “Use the currently used source attribute”. So as long as the columncoloris being processed, the target attribute is alsocolor, description is processed in the same way.$(current())in the value assignment gets the value(content) of the current source attribute. Then an underscore and the current date are added.
For
$(current())you can also write$()for short.
- the output data at the input of the transformation
- the changed data at the output of the transformation. The bottom line is that the multi-rule has done nothing other than add an underscore and the current date to the data in the
coloranddescriptioncolumns.
Examples of the source attribute filter:
Placeholder, simple specifications and regex is possible
| expression | result |
|---|---|
color, description |
All attributes containing color or description are processed. But colorful would also be recorded. |
* |
All existing attributes are processed |
\b[A-Za-z]+\b |
A regular expression: All attributes that only contain upper and lower case letters are processed. If a digit or a special character occurs, the attribute is ignored. |
\bcolor\b |
Only the attribute color is processed, colorful is ignored in this case |
\bcolor\b|\bdescription\b |
Exactly color and description are processed, colorful is ignored. |